Introduction: At the Seattle summit in May 2024, Oracle’s senior executives briefed a select group of industry analysts on OCI’s strategy. The presentation covered key areas such as infrastructure, sales differentiators, customer success, and a customer panel discussion. The focus was on OCI’s unique high security and privacy selling points combined with a distributed cloud strategy. OCI services are widely used in various deployments, from public and sovereign cloud to cloud at customer, dedicated regions, and Oracle Alloy. While the OCI strategy caters to diverse customer needs, this report will emphasize the significant focus areas.
Building data centers at speed: Clay Magourk, EVP of OCI, shared the OCI growth across revenue and customers, requiring additional data centers. Mahesh Thiagarajan, EVP of OCI Core Infrastructure, spoke about Oracle’s strategic and rapid data center construction. The accelerated capability comes from process improvements in tasks required to design and deploy a data center into production, ranging from time to generate data hall diagrams to validating GPU clusters. With vendors playing a significant role in any data center construction effort, supply chain optimization for faster delivery is essential. Oracle stressed the importance of building more inventory with new strategic reserves for future expansion plans, instilling confidence in the audience about OCI’s growth strategy.
While data center construction may seem straightforward, optimizing the process is crucial for an organization preparing for growth. Oracle highlighted the increasing power demand, expected to triple from 2024 to 2029. The company’s strategy of planning locations based on power availability is a critical factor in its ability to expand among leading public cloud providers.
Delivering AI capabilities:
The demand for AI solutions is growing, and hyperscale cloud vendors are racing to grow infrastructure to meet customer requirements. As a result, capital spending by cloud providers is increasing as demand is outpacing the available AI infrastructure capacity. Oracle shared the core AI infrastructure differentiators of OCI as:
- Speed: Delivering large GPU deployments in time.
- Performance: Scaling for large-scale Gen AI training and sustained model floating point utilization.
- Health: Enabling customers to finish multi-week or multi-month training at a higher than 95% rate.
- Price: Lower cost per port.
One of the innovations shared was having bare metal compute available, which enables isolation and security as it runs only a specific customer workload. This capability is vital to AI customers who pay close attention to safeguarding individual data. Another capability was defining the size and shape of GPU memory, which supports small language models to large language models in the 100B+ parameter AI model.
Oracle’s AI infrastructure is versatile for customers. It can scale and support compute powered by Intel and NVIDIA, with AMD support planned in the future.
Choices for OCI Services:
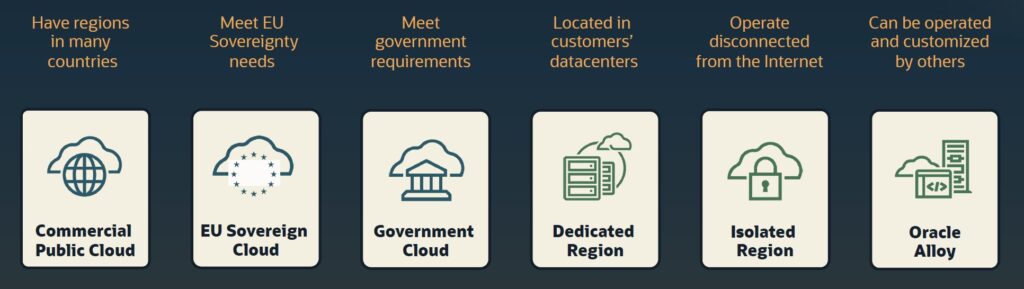
Users have varied needs when using cloud services. Data privacy and security issues drive cloud vendors to ensure data is stored, processed, and managed within a specific country’s borders, leading to the need for sovereign clouds. Some customers like to have their own data center but with services available on public clouds. Independent partners must provide their customers with cloud services without the required high investment.
During the summit, Oracle shared how OCI meets customers’ needs (Figure 1 above).
- Oracle EU Sovereign Cloud provides cloud services with complete operational control to meet data residency and compliance requirements. The infrastructure offers flexibility through various deployment models, ensuring organizations maintain sovereignty while accessing Oracle’s cloud services, APIs, and service-level agreements (SLAs).
- OCI Dedicated Region offers an OCI cloud region in your data center. It provides the benefits of the OCI public cloud while giving customers control over data and applications to meet security, regulatory, and data residency requirements. OCI public cloud services enable the modernization of infrastructure and applications with a consistent platform across both public cloud and on-premises environments.
- Oracle Alloy is a cloud infrastructure platform that enables partners to become cloud providers, offering Oracle cloud services and customized cloud services built by the partner. This platform allows partners to customize their commercial and customer experiences, control operations, and create new services tailored to specific market needs, all while maintaining stringent security and compliance standards without significant investments.
Oracle is the only cloud vendor that provides such a set of customer options. In the long run, this strategy could help Oracle in the following ways:
- AI where customers need it: While customers would like to reap the benefits of AI, one issue is training it on their data. The Oracle distributed cloud options address data location and operational control of AI workloads.
- Feedback for improvement: Lessons learned from customer and partner experience can help Oracle prioritize improvements to OCI services.
- Revenue growth: Partners using OCI to develop and deliver white-label end-to-end cloud solutions to customers can bring new revenue sources to Oracle.
Conclusion: Oracle’s comprehensive OCI strategy offers a range of deployment options tailored to meet diverse customer needs, emphasizing security, privacy, and flexibility. The Seattle summit showcased OCI’s strengths, including rapid data center construction, innovative AI infrastructure, and versatile service offerings such as Oracle EU Sovereign Cloud, OCI Dedicated Region, and Oracle Alloy. These capabilities enable customers to maintain data sovereignty, ensure compliance, and leverage advanced AI solutions. Oracle’s unique approach addresses current market demands and positions the company for sustained growth by fostering customer feedback, enhancing service quality, and generating new revenue streams through strategic partnerships.
Oracle’s multi-cloud strategy differs from that of major cloud providers. Recent wins at Fujitsu and Nomura Research in Japan show the worldwide partner momentum. General Dynamics Electric Boat and Aramco are implementations for dedicated regions. Palantir is delivering AI services to the government using Oracle’s AI infrastructure. If Oracle’s distributed cloud strategy increases its market share, competitors will likely offer similar capabilities.
